Amazon’s use of generative AI to enhance product reviews and Snap’s chatbot glitch made AI news this week. OpenAI introduces moderation with GPT-4, and Anthropic secures significant funding. Eth Zurich’s door-opening robot innovation stands out. Google enhances its Search AI, while Google Photos gains memory features. Opera’s iOS app integrates AI assistance, and EPFL develops apps aiding the visually impaired. SIGGRAPH showcases AI’s role in VFX and typography. Brain science meets AI in music interpretation and astrocyte research. CMU and Meta develop a learning robot mimicking toddler behavior.
Staying up-to-date in the swiftly evolving AI industry can be quite a challenge. Until AI itself takes on the task, here’s a convenient recap of last week’s happenings in the machine learning world, including noteworthy research and experiments that didn’t receive individual coverage.
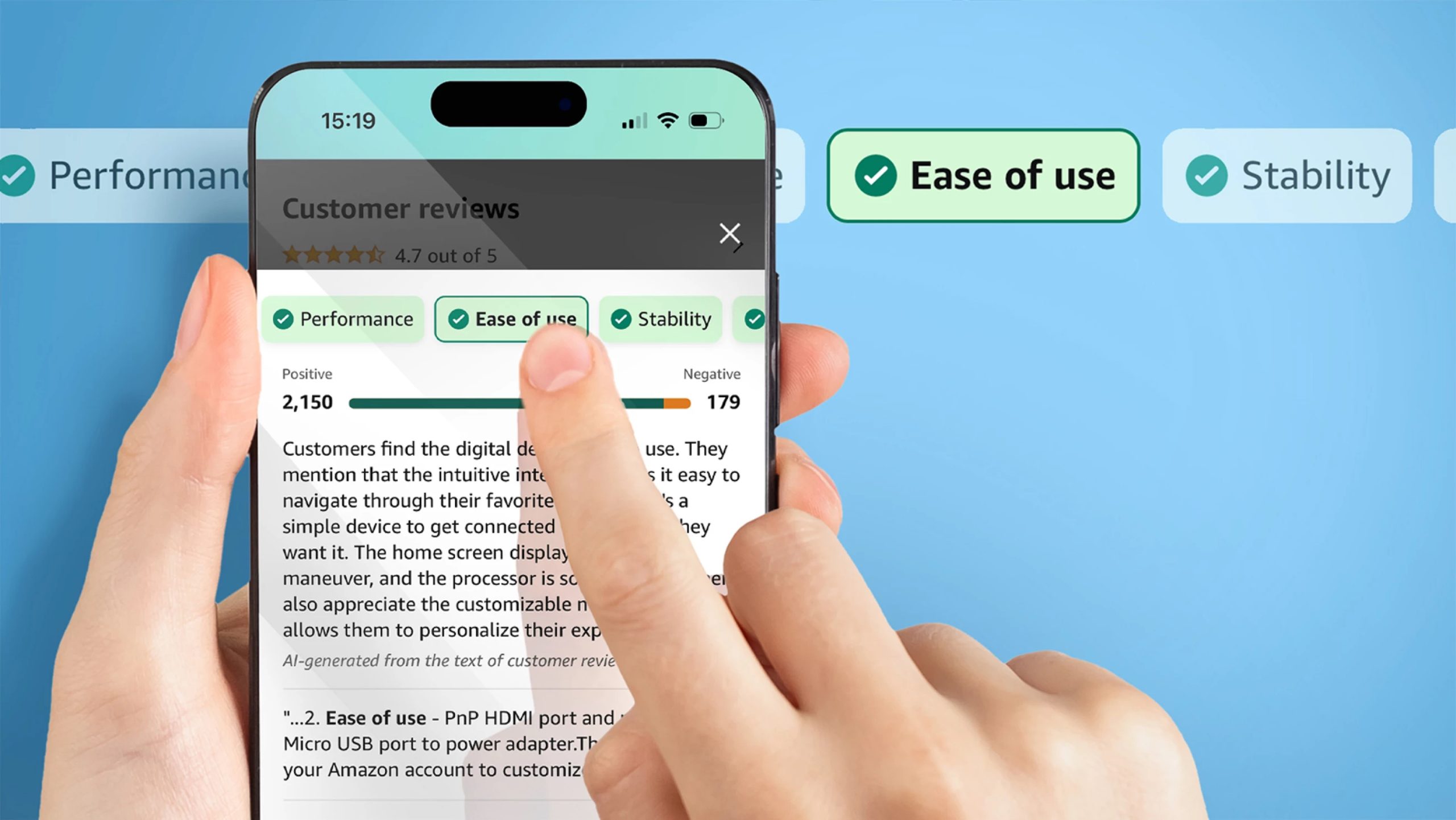
Amazon made headlines in AI this week by announcing its intention to leverage generative AI to “enhance” product reviews. Once implemented, this feature will add a concise paragraph to product detail pages, highlighting key product capabilities and customer sentiments extracted from reviews.
This enhancement sounds promising, particularly for both shoppers and sellers. However, what about the reviewers themselves?
I won’t argue that Amazon reviews reach the level of high art. Quite the opposite; a significant number of reviews on the platform are either fake or AI-generated.
Yet, some reviewers invest time and effort into crafting reviews that not only inform but also entertain. These reviews are more than just summaries and provide valuable insight and context. Attempting to condense these reviews through AI summarization would overlook their richness and depth.
Perhaps you’ve come across these gems, often found in book and movie review sections. These sections tend to attract more verbose Amazon reviewers, based on my anecdotal observation.
Consider, for instance, the review by Amazon user “Sweet Home” for J.D. Salinger’s “The Catcher in the Rye,” which spans over 2,000 words. This review delves into references to literary figures like William S. Burroughs, Jack Kerouac, George Bernard Shaw, Gary Snyder, and Dorothy Parker. Rather than being a simple review, “Sweet Home” offers a detailed analysis that contextualizes the novel’s themes to elucidate its lasting impact.
Similarly, Bryan Desmond’s review of the complex Thomas Pynchon novel “Gravity’s Rainbow” extends to 1,120 words. While it covers the book’s highlights and drawbacks, it goes beyond and delves into Desmond’s personal experience reading the book.
Could AI summarize these reviews? Certainly. However, it would come at the expense of the nuances and insights provided by the reviewers.
Amazon doesn’t plan to replace reviews with AI-generated summaries, but there’s concern that reviewers might lose motivation to invest substantial time and effort if their work goes largely unnoticed by the average shopper. This is an ambitious experiment, and only time will reveal its impact, as is often the case with applications of generative AI.
Here are some other noteworthy AI stories from the past week:
Snapchat’s AI Goes Off Track: Snapchat’s My AI feature, an in-app AI chatbot launched this year, had a brief glitch where it created its own Story and stopped responding to user messages. Snap, Snapchat’s parent company, confirmed it was a bug.
OpenAI’s New Moderation Technique: OpenAI introduces a content moderation method using GPT-4, its flagship generative AI model, to ease the workload on human moderation teams.
OpenAI’s Acquisition: OpenAI acquires Global Illumination, a New York-based startup specializing in AI-driven creative tools, infrastructure, and digital experiences. This marks OpenAI’s first public acquisition in its approximately seven-year history.
A New LLM Training Dataset: The Allen Institute for AI releases a substantial text dataset for large language models (LLMs), similar to OpenAI’s ChatGPT. Named Dolma, this dataset is meant to support the institute’s planned open language model or OLMo.
Robotic Advancements: Researchers at ETH Zurich develop a technique to teach robots tasks like opening doors. The system is adaptable to different robot designs and form factors.
AI Assistant for Opera: Opera’s iOS web browser app now integrates Aria, an AI assistant developed in collaboration with OpenAI, providing users with AI-powered browsing support.
Google’s AI Summaries: Google enhances its AI-powered conversational mode in Search, offering tools like term definitions and cross-language coding information to aid users in understanding web content.
Google Photos Embraces AI: Google Photos introduces the Memories view, allowing users to relive and share memorable moments through a scrapbook-like timeline.
AI Investment in Anthropic: Anthropic, an AI startup founded by former OpenAI leaders, secures $100 million in funding from South Korea’s SK Telecom, following its earlier Series C funding round.
AI’s Impact at SIGGRAPH: AI takes center stage at SIGGRAPH, serving as both a tool and research subject for VFX artists. Notable innovations include advancements in image generation models and applications in typography.
Innovations in Brain Science and AI: Researchers interpret brain activity using machine learning while listening to music, shedding light on neural clusters related to rhythm, melody, and vocals. MIT and Harvard explore the link between AI concepts and astrocytes, brain cells that may function similarly to attention mechanisms. Yale’s study shows ML’s adaptability in improving data quality from consumer wearable devices.
AI Assists Visual Impairments: EPFL students create apps assisting the visually impaired, guiding users to empty seats, and providing essential information from medicine bottles.
RoboAgent Learns like a Toddler: CMU and Meta collaborate on “RoboAgent,” aiming to teach robots everyday skills through observation and interaction, akin to a child’s learning process.
