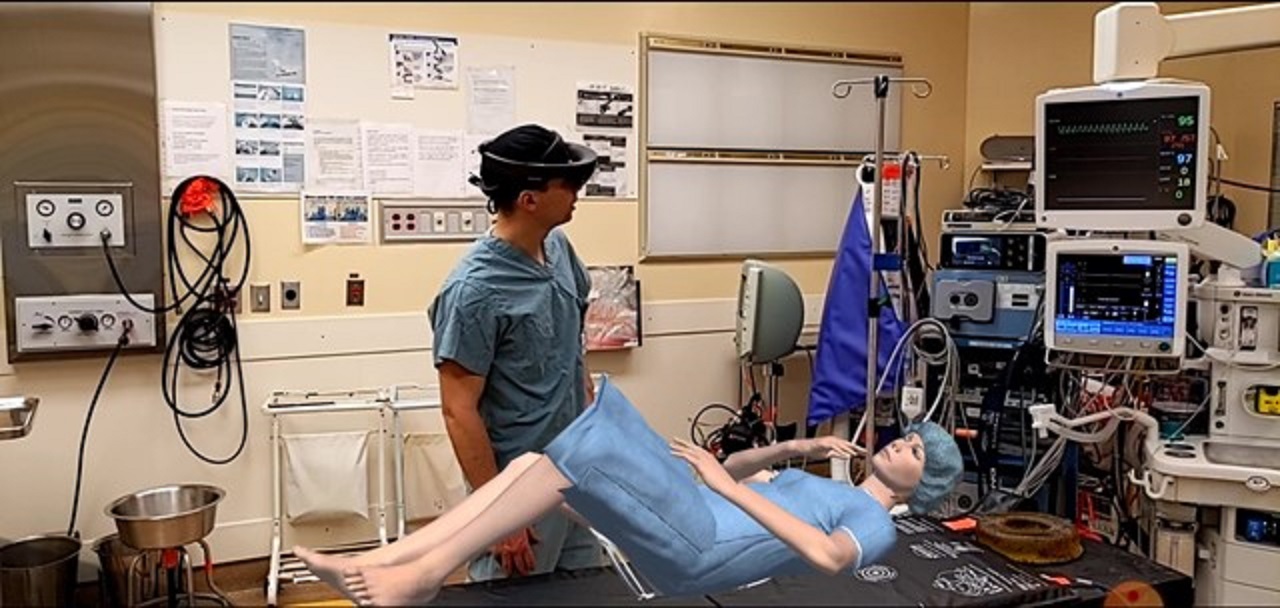
Discover how Mass General Brigham pioneers augmented reality (AR) for nursing education. Through immersive experiences, AR enhances training, reduces costs, and fosters a dynamic learning environment. Learn from their feasibility study at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, where AR revolutionized code cart training for nurses. Uncover the promises and challenges of AR in healthcare training and its potential to reshape clinical education. Join the journey towards a future where AR empowers the next generation of nursing leaders.
Augmented reality (AR) emerges as a groundbreaking tool in healthcare training, promising to revolutionize how nurses learn and practice. Mass General Brigham leads the charge in leveraging AR to transform nursing education, fostering immersive and personalized learning experiences. In this exploration, we delve into the innovative initiatives spearheaded by Mass General Brigham, particularly their groundbreaking feasibility study at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Through AR, they’re reshaping the landscape of nursing training, offering insights into the vast potential and challenges of integrating AR into clinical education.
The integration of augmented reality (AR) and other immersive technologies is revolutionizing various aspects of healthcare, offering significant advantages such as shorter training periods, enhanced clinician satisfaction, and dynamic learning environments. Mass General Brigham (MGB) innovation leaders are set to showcase these benefits at HIMSS24.
Once considered futuristic, extended reality (XR) – encompassing virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality – has become increasingly commonplace within healthcare settings, delivering tangible benefits for both patients and providers.
Among the most notable areas experiencing substantial innovation is the education and training of clinical staff. At the upcoming HIMSS24 conference in Orlando, innovation leaders from Mass General Brigham will present findings from a recent feasibility study conducted at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, demonstrating the vast potential of AR in code cart training for newly recruited nurses.
The presentation will delve into the collaborative efforts between clinical and IT professionals to develop an AR application tailored to enhance nurse onboarding and training. Early results have showcased significant improvements, with staff reporting heightened satisfaction levels, reduced training durations, and decreased inquiries regarding procedural complexities. Educators within MGB view AR training as a transformative shift in staff development and are exploring broader applications across the organization.
We caught up with Jonathan Letourneau, an innovation analyst at Mass General Brigham, and Chenzhen Cao, MGB’s Digital Innovation Hub manager, who provided insights into their upcoming session, “Training the Next Generation of Nursing Leaders Using Augmented Reality.”
Q. How promising are XR and AR for nursing training, and what are some of the most potential use cases?
A. XR technologies offer promising prospects for medical education and training, providing immersive, detailed, and personalized learning experiences that closely simulate the nursing workflow. Currently, we’re exploring scenarios depicting patient interactions to enhance practical skills acquisition. Despite facing technical and financial barriers, we’re leveraging web XR to develop discrete applications, such as a virtual code cart integrated into nurse education at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Q. What advantages do these technologies offer for training purposes?
A. XR facilitates immersive learning experiences, enhancing knowledge retention through interactive modules while reducing material costs associated with traditional training methods. This shift from lectures to virtual experiences not only improves educational outcomes but also mitigates medical waste generated from purchasing new equipment for training sessions.
Q. Can you provide background on your AR initiatives at Brigham and Women’s, particularly the feasibility study on code cart training?
A. Over a year and a half, our team explored various XR applications within healthcare, fostering internal engagement through community events. The study at Brigham and Women’s Hospital underscored the value of a distributed digital solution in nursing education, addressing resource constraints and enhancing learning flexibility.
Q. What were the opportunities and challenges identified during the study? Any surprises?
A. The study highlighted the scalability of digital platforms in nursing education, offsetting costs and waste associated with traditional methods. However, replicating tactile experiences, like inserting a needle, remains challenging due to haptic feedback accuracy limitations.
Q. How did nurses and clinical staff respond to the AR training?
A. Feedback from nursing colleagues has been overwhelmingly positive, leading to the expansion of AR initiatives within our organization. Nurses appreciate the personalized learning experience and the convenience of accessing training materials on their devices.
Q. How do you envision AR shaping healthcare training and processes in the future?
A. AR’s evolution promises interactive and responsive training scenarios, offering near-real-world experiences without patient risk. This approach has the potential to revolutionize training across various clinical domains, enhancing skill development and improving patient care outcomes.
Q. Any final thoughts or hopes for session attendees?
A. We hope our session inspires healthcare organizations to embrace XR technologies as integral components of their training toolkit. With mature technology and resources available, now is the opportune time for widespread adoption, offering substantial benefits in workforce development, infrastructure, and financial management.
As healthcare continues to evolve, the integration of augmented reality (AR) into nursing education stands as a beacon of innovation. Mass General Brigham’s pioneering efforts demonstrate the transformative impact of AR on training effectiveness, cost efficiency, and learner engagement. Despite challenges, AR holds immense promise in revolutionizing clinical education and preparing nurses for the complexities of modern healthcare. With ongoing advancements and widespread adoption, AR is poised to redefine the future of nursing training, empowering the next generation of healthcare leaders to excel in their roles.




